
Putting these pieces together gives the name carbon tetrachloride for this compound. Introduction to biological macromolecules. Putting these pieces together gives the name carbon tetrachloride for this compound. The second element, chlor ine, becomes chlor ide, and we attach the correct numerical prefix (tetra-) to indicate that the molecule contains four chlorine atoms. The second element, chlor ine, becomes chlor ide, and we attach the correct numerical prefix (“tetra-”) to indicate that the molecule contains four chlorine atoms. The name begins with the name of the first element-carbon. Let us practice by naming the compound whose molecular formula is CCl 4. *This prefix is not used for the first element’s name. This phenomenon is due to the opposite charges on each ion.Ĭovalent bonding is the sharing of electrons between atoms.\): Numerical Prefixes for Naming Binary Covalent Compounds Number of Atoms in Compound Most ionic compounds tend to dissociate in polar solvents because they are often polar. At the ideal interatomic distance, attraction between these particles releases enough energy to facilitate the reaction. However, this reaction is highly favorable because of the electrostatic attraction between the particles.


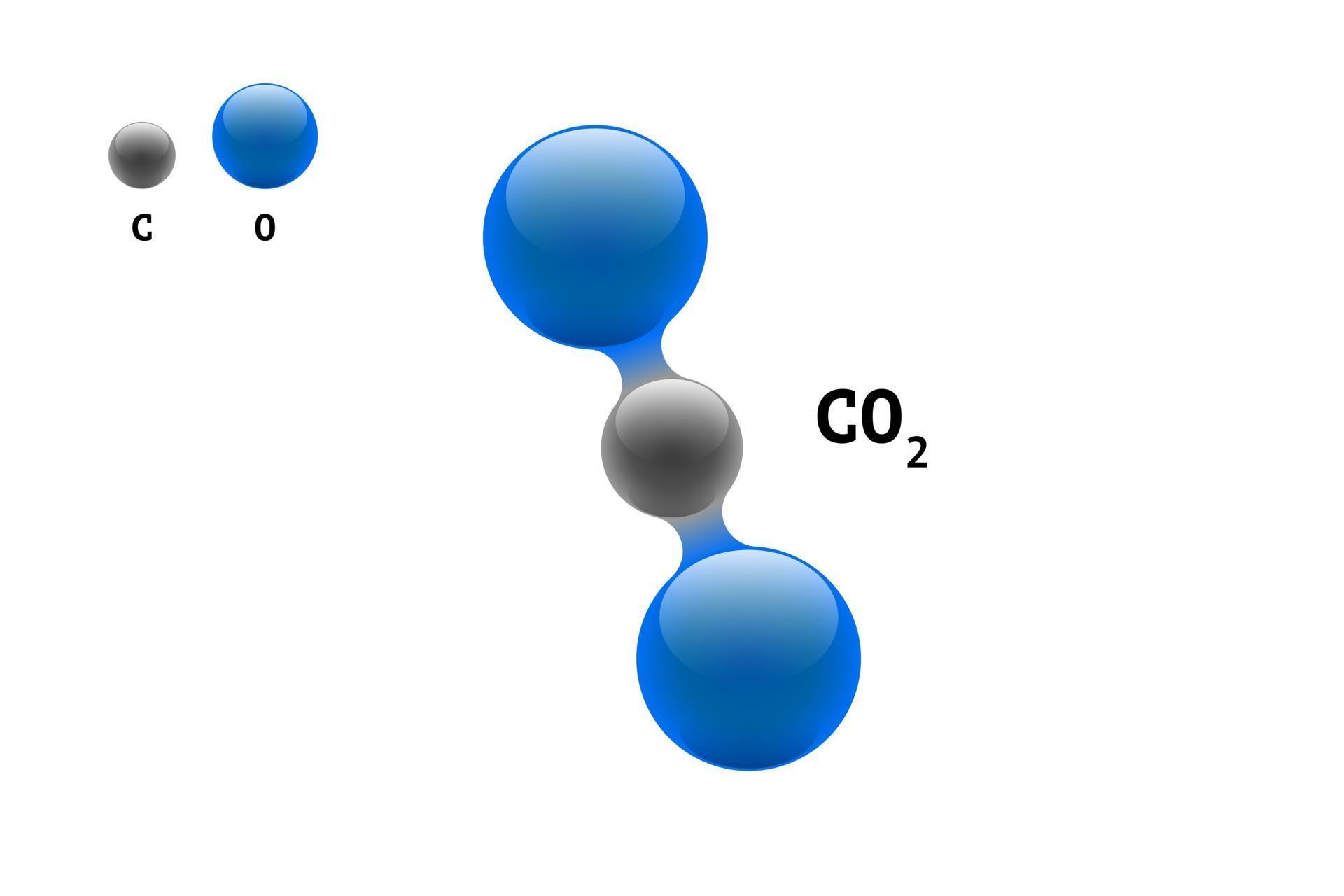
The predicted overall energy of the ionic bonding process, which includes the ionization energy of the metal and electron affinity of the nonmetal, is usually positive, indicating that the reaction is endothermic and unfavorable. This chlorine atom receives one electron to achieve its octet configuration, which creates a negatively charged anion. This creates a positively charged cation due to the loss of electron. This sodium molecule donates the lone electron in its valence orbital in order to achieve octet configuration. In ionic bonds, the net charge of the compound must be zero. The charges on the anion and cation correspond to the number of electrons donated or received. In ionic bonding, more than 1 electron can be donated or received to satisfy the octet rule. Similarly, carbon dioxide, which contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms in each molecule, is written as CO2. Similarly, nonmetals that have close to 8 electrons in their valence shells tend to readily accept electrons to achieve noble gas configuration. Determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar. By losing those electrons, these metals can achieve noble gas configuration and satisfy the octet rule. Explain how polar compounds differ from nonpolar compounds. To tell if CO2 (Carbon dioxide) is ionic or covalent (also called molecular) we look at the Periodic Table that and see that C is a. Ionic bonding is observed because metals have few electrons in their outer-most orbitals. Ionic bonds require an electron donor, often a metal, and an electron acceptor, a nonmetal. A molecule is polar if the shared electrons are equally shared. The Octet rule only applys to molecules with covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively charged cation, whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion. Which of the following statements are true (There can be more than one true statement.) A covalent bond is the same as a ionic bond. Because sodium is a metal and we recognize the formula for the phosphate ion, we know that this compound is ionic. The elements in Na 2 O are a metal and a nonmetal, which form ionic bonds. It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Is each compound formed from ionic bonds, covalent bonds, or both Na 2 O. Ionic bonding is the complete transfer of valence electron(s) between atoms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
